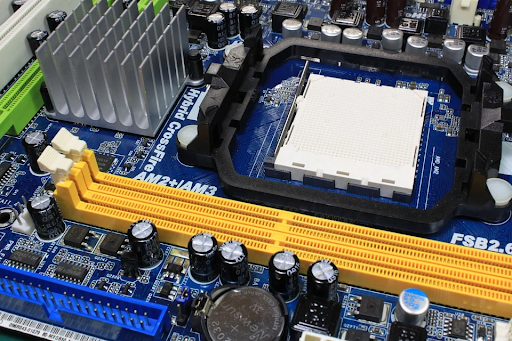
A motherboard is the part of a computer which connects every other component in the system. The motherboard contains all of the necessary components, such as CPU, RAM, hard drive and graphics card. Without it, your computer would not function at all!
The article will go on to explain what each component does and how they interact with one another through the motherboard made by FS PCBA.
There are many socket types for different socket processors.
CPU:
CPU/Processor can be found on the motherboard, it is removable and plugs into a slot (Socket) made specifically for that type of CPU. The motherboard determines which type of CPU you can fit to it and what speed they run at.
RAM:
RAM slots are also required components on any motherboard, as without them there would be no way to store data or instructions; these must fit into specific slots as dictated by the board’s requirement list, though one will generally find DDR3 memory matching up with most boards today.
Hard drive:
Hard drives need to connect through SATA ports on the motherboard, and require a power source so they can function properly. Some boards will come with on-board graphics which can be activated in some motherboards to save money and space.
I/O port:
Every motherboard will have USB ports of some sort, these are used to connect things like mice, keyboards and other peripherals.
Sound card:
Some motherboards feature on-board sound cards which can be switched on or off in the BIOS depending on preference.
Southbridge/northbridge:
One of the most important components is southbridge/northbridge. This is responsible for providing a connection from your CPU to all other peripherals. It is very important as it can provide a bottleneck in some cases, with higher-end CPUs having bigger connections with plenty of bandwidth.
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System):
This is the system which boots your computer and controls all hardware configuration. It can be accessed by pressing a certain key as the computer boots (Delete, F2 etc.) and contains all hardware information such as CPU speed, memory speed and current specs. It also manages overclocking features if available on your motherboard. If you need Computer Support or any help related to your business get from here.
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) slot:
These slots are used on some motherboards to place graphics cards without using PCI-e or PCI ports.
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) slots:
These allow for expansion of the motherboard through the addition of extra components such as sound cards, graphics cards etc.
SATA (Serial ATA):
This allows for data transfer of hard drives and optical drives. It is faster than its predecessor PATA connections which it mostly replaced, but can be more difficult to configure correctly depending on your operating system/motherboard combination. eSATA is essentially SATA with an e at the beginning instead of a regular s; this version is backwards compatible with all SATA devices but has lower throughput speeds than the regular SATA which is of no concern on external devices.
PATA (Parallel ATA):
This enables your motherboard to access data from optical drives and hard drives by transferring information in parallel. It can be tricky to configure correctly on some operating systems, but you should refer to the manual for more information on that topic.
PCI-e slots:
These are used for graphics cards or network cards, depending on which PCI-e slot you choose. They replace the AGP slot as it has much higher throughput speeds than its predecessor.
USB ports:
As the name suggests, these allow for USB connectivity with your PC; this allows many components to function properly through the installation of drivers which may otherwise not work without them.
CPU socket:
This is where the CPU connects to the rest of your motherboard. If you require more information on this topic, refer to your manual or Google it for more details. This changes depending on what you are using.
Sockets come in various shapes and sizes, but if you know what kind of processor requires what type of socket then you should be able to figure out whether or not a certain board will work with your computer parts.
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit):
These allow for high performance processing of graphics and often have their own supply of memory which can free up system resources such as RAM and reduce load times etc. They connect with PCI-e ports but may also use DDR3 memory slots instead of the system memory slots.
Conclusion
The motherboard is an essential part of every computer system. Without one your computer would not function at all! It allows all components to communicate with each other through a series of wires, switches and circuits. Motherboards generally last around 4 years before becoming outdated and requiring replacement. All information for this article was gathered through various sources that I have credited throughout my page. Please feel free to comment if you have any further questions about motherboards or any feedback. Thank you for